HackerRank-BasicJoin-Challenges
Challenges
Julia asked her students to create some coding challenges. Write a query to print the hacker_id, name, and the total number of challenges created by each student. Sort your results by the total number of challenges in descending order. If more than one student created the same number of challenges, then sort the result by hacker_id. If more than one student created the same number of challenges and the count is less than the maximum number of challenges created, then exclude those students from the result.
Input Format
The following tables contain challenge data:
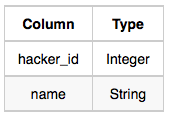
- Hackers: The hacker_id is the id of the hacker, and name is the name of the hacker.
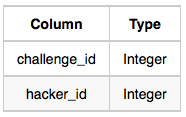
- Challenges: The challenge_id is the id of the challenge, and hacker_id is the id of the student who created the challenge.
Sample Input 0
Hackers Table:

Challenges Table:

Sample Output 0
21283 Angela 6
88255 Patrick 5
96196 Lisa 1
Sample Input 1
Hackers Table:

Challenges Table:

Sample Output 1
12299 Rose 6
34856 Angela 6
79345 Frank 4
80491 Patrick 3
81041 Lisa 1
Explanation
For Sample Case 0, we can get the following details:

Students 5077 and 62743 both created 4 challenges, but the maximum number of challenges created is 6 so these students are excluded from the result.
For Sample Case 1, we can get the following details:

Students 12299 and 34856 both created 6 challenges. Because 6 is the maximum number of challenges created, these students are included in the result.
My solution
SELECT hacker_id, max(name) as max_name, count(hacker_id) as count_id
FROM
(
SELECT row_number() over(partition by h.hacker_id order by h.hacker_id) as rownumber, h.hacker_id, h.name
FROM Hackers h, Challenges c
WHERE h.hacker_id = c.hacker_id
)
GROUP BY hacker_id
HAVING count(hacker_id)=(
SELECT MAX(cnt)
FROM (
SELECT COUNT(hacker_id) as cnt
FROM Challenges
GROUP BY hacker_id
)
)
OR count(hacker_id) in
(
SELECT cnt
FROM (
SELECT COUNT(*) as cnt
FROM Challenges
GROUP BY hacker_id
)
GROUP BY cnt
HAVING COUNT(cnt)=1
)
ORDER BY count_id DESC, hacker_id;

Comments